
Docket No.: 1857, second instance (终), civil case (民), (2019) Guangdong Higher People's Court (粤)
Lower Court Docket No.: 1211, first instance (初), civil case (民), (2017) Guangzhou Intellectual Property Court (粤73)
SUMMARY OF THE ARGUMENT
If the right holder of a well-known trademark files a civil lawsuit with the court in the course of administrative litigation with the trademark infringer with respect to the validity of the alleged infringing registered trademark and requests the infringed infringer to stop the infringement act and compensate for its loss, the people's court shall accept the case, and shall not reject the case on the ground that it is a dispute between two registered trademarks. In those cases involving the aforementioned issues, the right holder of a well-known trademark is entitled to request the recognition of a well-known trademark and the special protection of the distinctiveness of the well-known trademark, even if the lawsuit is filed by the right holder against the infringement act of using the well-known trademark on the identical or similar goods.
STATEMENT OF THE CASE AND FACTS
LOUIS VUITTON MALLETIER
Plaintiff-Appellant
v.
GUANGZHOU RUIWANG LEATHERWARE CO., LTD.,
Wang X,
Defendants-Appellees
On January 15, 1986, Louis Vuitton Malletier was granted by the Trademark Office of China of the exclusive right to use the trademark "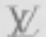 ", which has become a well-known trademark in China by 2012. On September 17, 2015, Wang X obtained the registered trademark "
", which has become a well-known trademark in China by 2012. On September 17, 2015, Wang X obtained the registered trademark "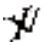 " (registration No. 11724660) assigned by others, and produced and sold handbags, wallets and other products using the aforementioned infringing mark through Guangzhou Ruiwang Leatherware Co., Ltd.. In addition to the alleged infringing trademark in this case, there are several other trademarks under Wang X's name that are similar to the"
" (registration No. 11724660) assigned by others, and produced and sold handbags, wallets and other products using the aforementioned infringing mark through Guangzhou Ruiwang Leatherware Co., Ltd.. In addition to the alleged infringing trademark in this case, there are several other trademarks under Wang X's name that are similar to the"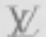 " trademark. On June 14, 2018, the Trademark Office issued a ruling declaring that the registered trademark "
" trademark. On June 14, 2018, the Trademark Office issued a ruling declaring that the registered trademark "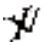 " (registration No.: 11724660) was invalid. Ruiwang refused to accept the ruling and filed an administrative lawsuit with the court. The court has not yet made a decision on the case.
" (registration No.: 11724660) was invalid. Ruiwang refused to accept the ruling and filed an administrative lawsuit with the court. The court has not yet made a decision on the case.
Louis Vuitton filed a lawsuit with Guangzhou Intellectual Property Court, requesting that its trademark in dispute be recognized as a well-known trademark and that Ruiwang and Wang X be ordered to stop their infringement acts and compensate for its loss. Ruiwang argued that this case belonged to the dispute between registered trademarks; according to the relevant laws, the people's court had no right to accept and hear this case.
Guangzhou Intellectual Property Court held in the first instance that after the invalid ruling was made, this case was not a dispute between registered trademarks and should be accepted by the court. Since the class of goods of the alleged infringing trademark in this case is identical with the approved scope of use of the trademark "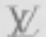 ", it is not necessary to recognize the well-known trademark. In summary, the court of first instance affirmed that Ruiwang constituted infringement, ruled that Ruiwang should stop its infringement act and that Ruiwang and Wang X should jointly compensate Louis Vuitton RMB 140,000, and rejected Louis Vuitton's other claims.
", it is not necessary to recognize the well-known trademark. In summary, the court of first instance affirmed that Ruiwang constituted infringement, ruled that Ruiwang should stop its infringement act and that Ruiwang and Wang X should jointly compensate Louis Vuitton RMB 140,000, and rejected Louis Vuitton's other claims.
Louis Vuitton, Ruiwang and Wang X all refused to accept the first instance judgment and appealed to Guangdong Higher People's Court. In the second instance, the Higher People's Court of Guangdong Province held that, Wang X filed an administrative lawsuit against the ruling which declared the invalidity of the trademark, and no legally effective judgment was made in the administrative lawsuit, so the aforementioned ruling did not take effect and this case still belonged to the dispute between the registered trademarks; in general such dispute would not be handled by the court. However, if the registered trademark in dispute was recognized as a well-known trademark and the owner of such trademark filed a lawsuit with the court in accordance with the relevant laws, the conditions for filing a lawsuit were met and the case should be handled by the court. The essence of well-known trademark protection is to better protect well-known trademark. Since Article 13(3) of the Trademark Law provides for the protection of well-known trademark against the infringement of trademark rights of non-identical and non-similar goods by recognizing the well-known trademark, a stronger protection can surely be given to well-known trademark with respect to identical or similar goods. In this case, Louis Vuitton claimed that its registered trademark "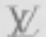 " was a well-known trademark, and that the alleged infringement act violated the provisions of Article 13 of the Trademark Law, constituting an infringement of the trademark right of the well-known trademark in dispute. In the course of this case, the alleged infringing registered trademark was still a valid registered trademark, and Louis Vuitton could not prohibit the use of the alleged infringing registered trademark on the grounds that the registered trademark "
" was a well-known trademark, and that the alleged infringement act violated the provisions of Article 13 of the Trademark Law, constituting an infringement of the trademark right of the well-known trademark in dispute. In the course of this case, the alleged infringing registered trademark was still a valid registered trademark, and Louis Vuitton could not prohibit the use of the alleged infringing registered trademark on the grounds that the registered trademark "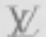 " was a general registered trademark. Ruiwang and Wang X even argued that this case should not be placed on file on the ground that the alleged infringing trademark was a registered trademark. Therefore, it is necessary to examine whether the registered trademark "
" was a general registered trademark. Ruiwang and Wang X even argued that this case should not be placed on file on the ground that the alleged infringing trademark was a registered trademark. Therefore, it is necessary to examine whether the registered trademark "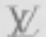 " was a well-known trademark in this case. The evidence in this case proved that the registered trademark "
" was a well-known trademark in this case. The evidence in this case proved that the registered trademark "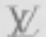 " was already a well-known trademark at the time of the infringement, and Ruiwang constituted an infringement of the trademark right and should stop its infringement act and compensate for the loss. In summary, the court of second instance ruled as follows: the first item of the first instance judgment should be affirmed; the third item of the first instance judgment should be abrogated; the second item of the first instance judgment should be altered, and Ruiwang and Wang X should jointly compensate Louis Vuitton for its economic losses and reasonable costs incurred for protecting its rights which amounted to RMB 500,000; other claims of Louis Vuitton should be rejected.
" was already a well-known trademark at the time of the infringement, and Ruiwang constituted an infringement of the trademark right and should stop its infringement act and compensate for the loss. In summary, the court of second instance ruled as follows: the first item of the first instance judgment should be affirmed; the third item of the first instance judgment should be abrogated; the second item of the first instance judgment should be altered, and Ruiwang and Wang X should jointly compensate Louis Vuitton for its economic losses and reasonable costs incurred for protecting its rights which amounted to RMB 500,000; other claims of Louis Vuitton should be rejected.
ANALYSIS
This case is a typical case involving both the right conflict of commercial marks and the protection of well-known trademarks. In recent years, some infringers maliciously register or assign infringing trademarks for goods which are in the identical or similar categories of the approved range of use of well-known trademarks so as to lean on famous brands. After the well-known trademark right holder applied for the invalidation of the alleged infringing trademark and the administrative organ made a ruling declaring invalidity of the trademark, some infringers obstructed the well-known trademark right holder from obtaining relief timely by filing administrative lawsuits so as to prolong the time for them to obtain improper gains. If the well-known trademark right holder files a civil lawsuit against the infringement act before the administrative litigation is closed, the civil lawsuit may not be accepted and the well-known trademark right holder may have no right to request for recognition of the well-known trademark in the case and get appropriate protection, which is very unfavorable to the timely and adequate protection of the well-known trademark.
In this case, the judgment of second instance, which is oriented towards strengthening the protection of well-known trademarks and cracking down on attaching other high-reputation trademarks, has made a useful exploration for properly resolving disputes involving both the protection of well-known trademarks and right conflict of commercial marks at the same time, effectively protecting well-known trademarks, cracking down on the impropriety of malicious trademark registration, purifying the market competition environment, playing the role of correctly guiding market players to operate in good faith, and achieving a good social effect, which is of reference significance to the trial of similar cases in the future.
|
Copyright © 2003-2018 China Intellectual Property Magazine,All rights Reserved . www.chinaipmagazine.com 京ICP备09051062号 |
|
|



